How underfloor Graphene heating can help the mission to net zero
Net zero is both an approach and a target that affects all areas of life. The ultimate goal is to consciously balance global greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. That requires us to match the amount of greenhouse gasses emitted into the atmosphere with the amount removed. Thus, a net zero approach may focus on measuring and reducing emissions across an entire value chain. This includes what the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol defines as Scope 2 and 3 emissions. Briefly:
- Scope 1: Emissions from sources owned or directly controlled by an organisation. These are generally associated with direct fossil fuel combustion.
- Scope 2: Emissions caused indirectly. These may relate to the combustion processes involved in producing the energy that a company uses.
- Scope 3: Emissions that an organisation is connected to via their value chain. These typically relate to the purchasing of products from third-parties, but include all emissions not covered in Scopes 1 and 2.
Minimizing the net impact of human activities on our climate is thus a multifaceted and holistic process. It is also integral to key climate change initiatives. Net zero is considered an important precursor to halting the rise of global temperatures, preferably to below 2°C as per the Paris Agreement. More companies are adopting proactive Environmental and Sustainability (ESG) goals to play their part. But decarbonising an entire value chain is not an easy fix.
Technological innovation is playing a central role in the net zero mission. It also sets the stage for functional graphene to deliver upon its early promise in a potentially remarkable way.
Heating and cooling are responsible for over 40% of global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Yet electricity grids in developed countries are increasingly electrified. Integrating that increased share of renewable electricity with greater efficiency space heating systems could mark a promising shift from "incumbent, heavily fossil-fuel dominated" heating systems. Graphene-based underfloor heating is an exciting avenue for that initiative.
Why Graphene?
Graphene's remarkable thermal conductivity allows for a rapid and uniform distribution of heat, which translates into reduced energy consumption for heating purposes. Traditional underfloor heating systems, whether hydronic (water-based) or electric, often require significant amounts of energy to maintain comfortable room temperatures. In contrast, graphene-based systems can achieve the same level of warmth with lower energy input due to graphene's efficient heat distribution capabilities.
Graphene is not only chemically inert and moisture resistant but also capable of reaching high functional temperatures up to 120°C, providing a durable and robust heating solution. The rapid thermal response of graphene, heating up to 60°C in just 60 seconds, coupled with its ability to distribute heat uniformly, eliminates hot spots and irregular heating zones common in traditional heating systems. This ensures a more consistent and comfortable indoor environment.
Revolutionizing Home Heating with Haydale’s Graphene-Based Ink
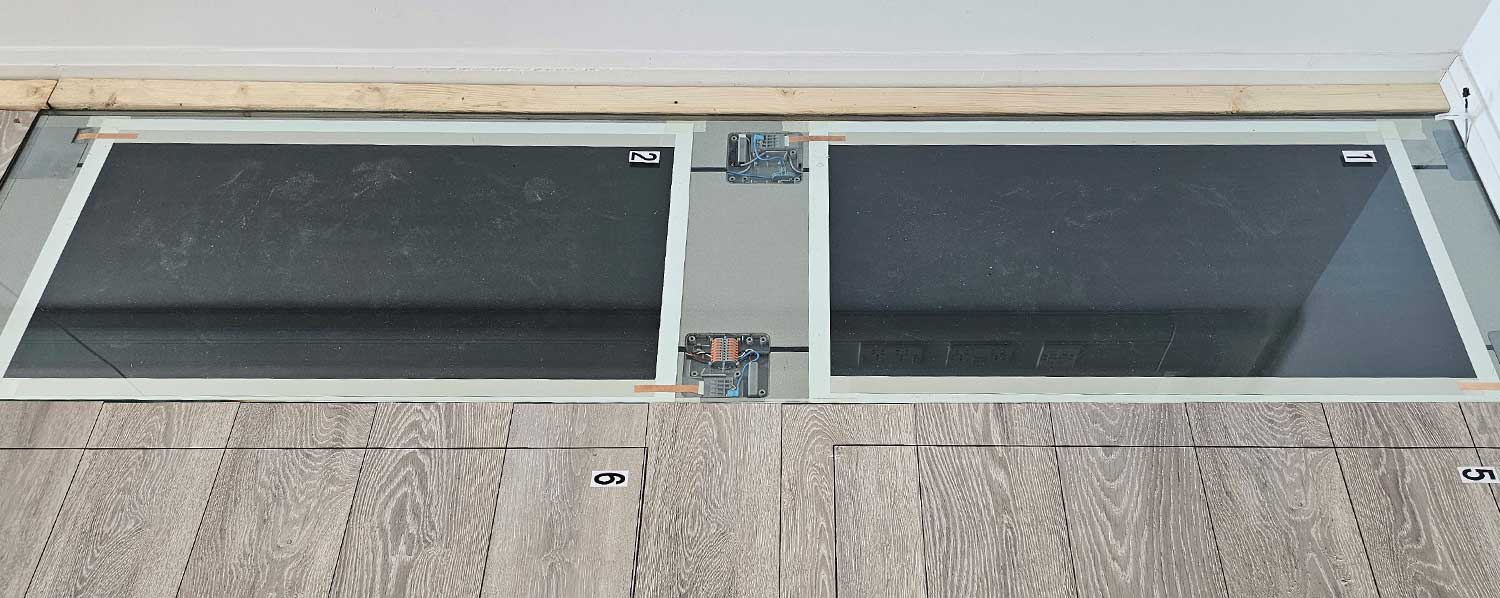

Haydale has teamed up with industry leader Staircraft to trial our unique graphene-based functional ink on their innovative flooring system. The results? A game-changing, energy-efficient heated flooring solution that's easy to install and cost-effective.
We’re thrilled to see our ink outperform competitors, delivering a flexible, reliable heating system that aligns with the drive toward Net Zero.
Curious about how Haydale’s innovation can transform home heating? Learn more.
How Does it Work?
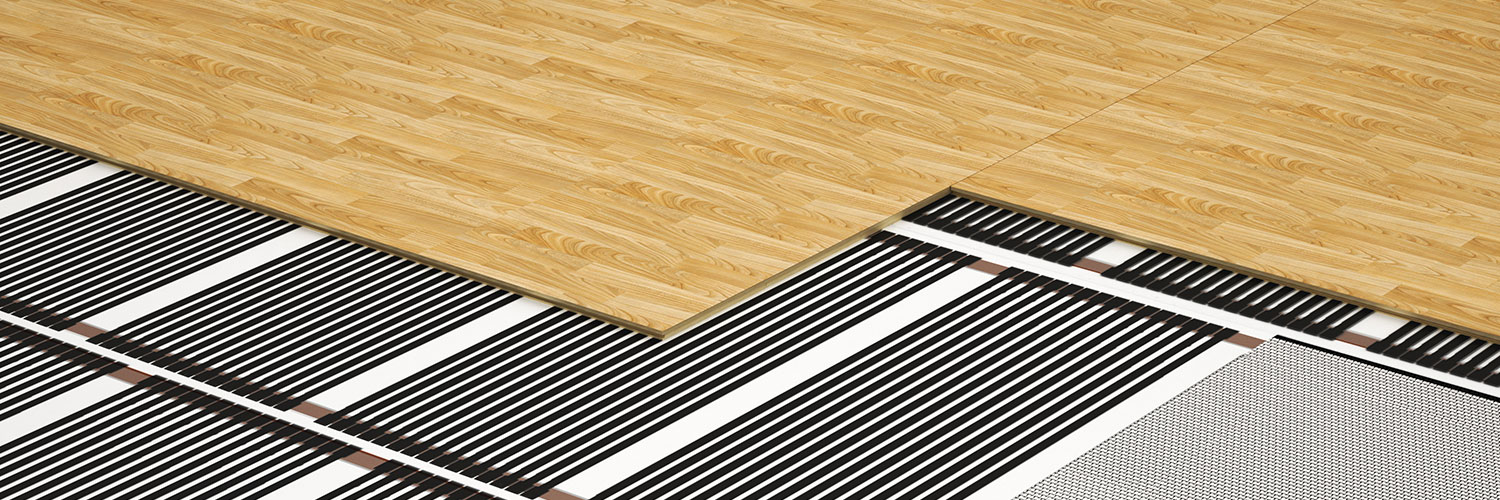
Graphene-infused heating elements are installed directly under flooring materials. Heating works similarly to traditional underfloor systems. Electricity passes through the element, generating heat via electrical resistance. Although graphene has a low resistance, its large surface area enables significant heat generation. This combines graphene's exceptional thermal conductivities to ensure rapid heat generation and uniform distribution. Coupling graphene underfloor heating with the right insulation materials and advanced thermostatic controls can enable accurate, programmatic heating in residential and commercial applications. Studies suggest that systems of this ilk could reduce energy consumption by up to 15% compared to conventional gas-powered systems.
Future Perspectives
As the global community strives to meet net-zero emissions targets, adopting innovative technologies like graphene-based underfloor heating systems is essential. Their ability to improve energy efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, and utilize renewable energy sources makes them valuable in the transition to a more sustainable future. They offer a unique approach for combatting emissions across the value chain, thus empowering organisations on their journey towards net zero.
At Haydale, we aim to demonstrate the power of graphene heater inks in energy applications. Our goal is to functionalise graphene materials for cutting-edge applications, and to realise the potential of this unparalleled nanomaterial.
References & Further Reading
- Pankaj Bhatia, et al. Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard. Greenhouse Gas Emissions Protocol. 2013. [Available: https://ghgprotocol.org/corporate-value-chain-scope-3-standard]
- Mathilde Fajardy, David M. Reiner. An overview of the electrification of residential and commercial heating and cooling and prospects for decarbonisation. University of Cambridge. 2021. [Available: https://www.econ.cam.ac.uk/research-files/repec/cam/pdf/cwpe20120.pdf]
